How Open Banking is Reshaping the Future of Financial Services
From seamless digital transactions to the rising popularity of the Buy Now Pay Later function, open banking has transformed the financial services industry.
Open banking is a system that allows banks and financial institutions to share customer data securely with third-party providers through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This has paved the way for innovative products and services, empowering consumers, and reshaping the landscape of the financial sector.
As per research, the current open banking market is valued at around $57 billion in 2023, and this could grow by 479% to reach $330 billion by 2027.
Read on to understand how open banking can be the focal point for the next big financial revolution and get a view of its benefits, use cases, challenges, and the future of this emerging technology.
Understanding Open Banking
Firstly, let us understand how open banking works.
In traditional banking, customer data is typically kept within the confines of individual banks, making it challenging for customers to access and manage their financial information across different institutions. In situations where data needs to be shared, traditional banking poses complexities.
For example, using a bank’s debit card to withdraw cash from another bank’s ATM, involves tedious processes that need to be done to track information, manage transaction history, and validate this transaction.
Open banking aims to transform this by creating an ecosystem where banks and other financial institutions can collaborate and share data with third-party providers, like Fintechs. Using API banking, allows customers to share their financial information securely with authorised third-party providers.
Thus, customers can grant permission to these third-party providers to access their financial data, including transaction history, account balances, and other relevant information. This data sharing is done in a secure, standardised, and efficient manner, improving customer experience.
Benefits of Open Banking
While traditional banking follows a more closed and centralised model, open banking embraces collaboration, data sharing, and innovation to offer customers a more personalised and inclusive banking experience.
This brings several benefits for customers and the financial services industry, which includes the following:
Enhanced Customer Experience (CX)
Open banking allows customers to have an overview of their finances across multiple accounts at one interface. This eliminates a lot of manual effort and hassle. It further makes seamless transactions, personal finance management, and more, possible. All of these result in a better customer experience.
Better Financial Services and Products
Open banking can help consumers find better financial services and products that are more aligned with their needs. This is because third-party providers can use consumer data to create more personalised and tailored services and products.
Reduced Costs
Since customer information can be shared easily and securely, businesses reduce costs by streamlining their operations. For example, open banking can be used to automate payments, reduce fraud, and improve compliance.
Innovation & New Services
Buy Now Pay Later, co-branded credit cards and so many new-age financial solutions are thriving, thanks to open banking. It facilitates the creation of innovative products and services that were previously inaccessible.
For instance, Hyperface utilises open banking to offer its customers seamless access to financial services within its platform. By utilising open APIs and SDKs, users can link their bank accounts, credit cards, and investments to get a comprehensive view of their finances.
This innovation, essentially allows financial institutions to leverage the Credit-card as a Service platform, to provide customisable experiences for their customers.
Open Banking Use Cases
Open banking opens Pandora’s box for possibilities, enabling financial services to explore newer and more efficient processes.
Some of the most common use cases where open banking can be leveraged include the following:
Personal Financial Management
With easy access to customers’ data and financial history, open banking can help consumers track their spending, set budgets, and identify areas where they can save money. Open banking puts the power back into the hands of customers.
Risk Management
By accessing real-time financial data through APIs, open banking allows financial institutions to perform more accurate risk assessments of customers. This helps them make informed and timely decisions regarding creditworthiness and fraud detection.
Credit Scoring
One key area where open banking can be used is to improve the credit scoring process. It provides lenders, like neobanks, with a complete picture of a borrower’s financial history, accelerating the decision-making process. This also makes it easier for borrowers to get approved for loans and credit cards.
Embedded Banking
It refers to integrating financial services into non-financial platforms, offering customers seamless access to banking and financial services within their everyday online experiences. For instance, AmazonPay provides customers with a streamlined and frictionless financial transaction experience on their platform itself.
Investing
Open banking can be used to make the rather lofty process of investment simpler. For example, open banking can be used to connect investment platforms to bank accounts, so that consumers can easily transfer money between their bank accounts and investment accounts.
Insurance
Open banking can be used to connect insurance platforms to bank accounts so that consumers can easily provide proof of income and other financial information when applying for insurance. This can also be used for other insurance processes like onboarding, claims settlement, and others.
Challenges & Solutions
Open banking could be the next realm of the financial space. But like with any new technology, open banking has a few challenges that need to be tackled for it to reach its complete potential. Some of these major challenges include:
Data Security & Privacy
One of the most pressing concerns with open banking is the security and privacy of customer data. Around 60% of financial institutions mentioned the time and effort required to protect, identify, and mask customer identities consistently while preserving referential integrity of data as the number one issue for embracing open banking fully.
As APIs expose sensitive financial information, any vulnerabilities or hacks could lead to massive data breaches and financial frauds.
To address this, financial organisations and third-party providers must enforce robust security protocols, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and stringent security audits.
Regulatory Compliance
Open banking is a relatively new technology, and there is still some uncertainty about the regulatory landscape. Additionally, businesses that are already participating in open banking initiatives have huge gaps.
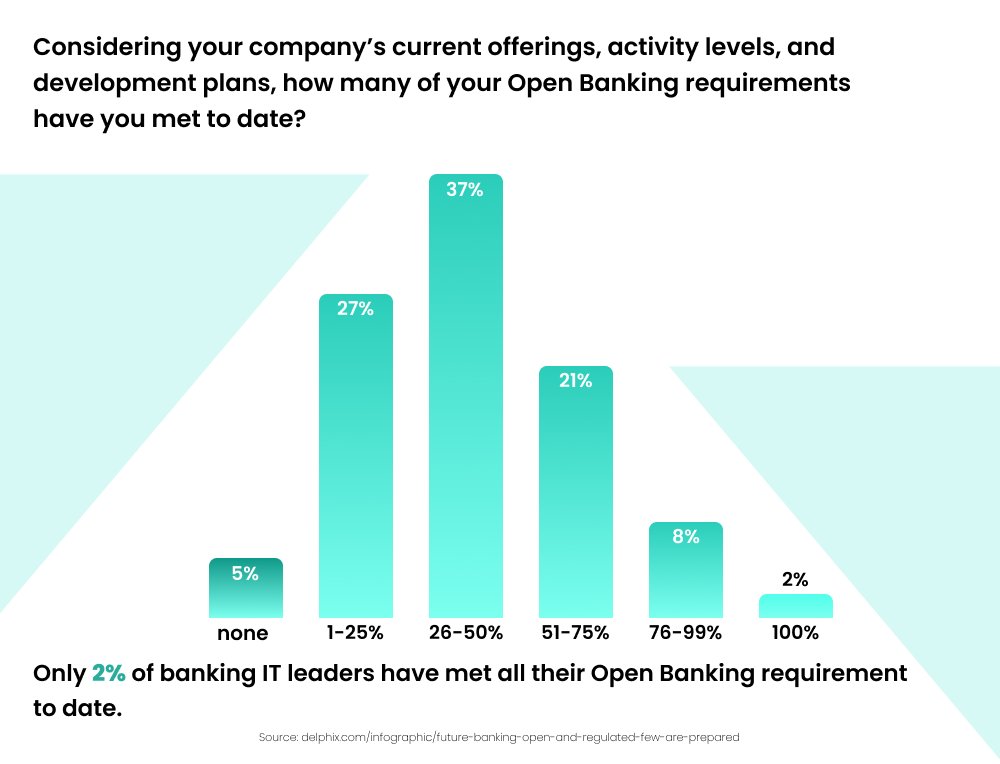
As per a report, only 2% of banking IT leaders have met all their open banking requirements to date, with 98% of financial organisations not being fully prepared for open banking regulations.
Businesses that want to participate in open banking need to make sure that they are compliant with all applicable regulations.
Customer Adoption & Education
When it comes to any financial process, adoption is always a big issue. The same is the case with open banking, given the lack of understanding and willingness of consumers to share their data with third-party providers.
Therefore, building trust through transparent communication and educating customers about the benefits and security measures of open banking is crucial. It is also essential to provide consumers with the right understanding of “do’s and don’t’s” with this technology, given the potential for fraud or misuse of private data.
The Future of Open Banking
Despite the challenges, there is light at the end of the tunnel for open banking. The number of open banking users worldwide is already growing and is expected to grow at an annual rate of nearly 50% between 2021 to 2024, with the total users predicted to reach 132.2 million by the end of next year.
Open banking is already being used in conjunction with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain. As these technologies evolve, the potential for open banking to explore unchartered territories only increases.
For example, AI and ML can be used to analyse consumer data and provide personalised financial advice. Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent financial transactions while securing customer information.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases emerge. By embracing emerging technologies and evolving regulatory frameworks, the global outlook for open banking looks promising and can present a future where financial services are more inclusive, personalised, and accessible.


